In free fall, we assume that there's no air resistance.
But, as we do not supply any initial velocity to the object, u = 0. So the equation becomes v = a . t
And since a = acceleration due to gravity, it's value is 9.81ms-2
Therefore, our final equation becomes v = 9.81 * t
This equation can be compared with y = mx + c where, c = 0. Now m = 9.81, which must be the gradient of the graph.
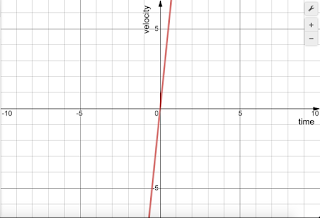 |
| Velocity vs Time Graph For Free Fall |
Hence, velocity vs time graph for free fall is a straight line with following properties:
- Passes through origin. Why? Because if you compare v = 9.81 * t with y = mx + c , you'll find that c = 0, which is the y-intercept. If a line has y-intercept of 0, it must go through origin.
- Has a gradient of 9.81, Why? Again if you compare v = 9.81 * t with y = mx + c , you'll find that m has a value of 9.81, which is the slope of a straight line.


Post a Comment